Alzheimer's disease, a progressive neurological disorder that causes brain cells to degenerate and die, is the most common cause of dementia among older adults. Diagnosing Alzheimer's disease involves a detailed evaluation, including medical history, physical exams, and possibly brain imaging and other tests. For families seeking Alzheimer's care services in Manhattan, medflyt service offers licensed caregivers who are trained to provide specialized care for Alzheimer's patients.

Initial Evaluation
The process of diagnosing Alzheimer's disease begins with a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional. This typically includes:
Medical History: The doctor will ask about the patient's past medical history, including any current symptoms, medication use, and family history of Alzheimer's disease or other dementias.
Physical Exam: A physical examination helps rule out other conditions that might cause similar symptoms, such as infections, vitamin deficiencies, or thyroid issues.
Neurological Exam: During this exam, the doctor assesses memory, problem-solving, attention, counting, and language skills.
Cognitive and Neuropsychological Tests
These tests assess the patient's cognitive functions, including memory, language skills, visual-spatial awareness, problem-solving, and other intellectual abilities. The results help determine if the symptoms are due to Alzheimer's or another condition.
Laboratory Tests
While there are no laboratory tests to diagnose Alzheimer's directly, blood tests and other lab work can help rule out other conditions that might mimic Alzheimer's disease, such as hormonal imbalances or nutritional deficiencies.
Brain Imaging
Brain imaging technologies can provide detailed images of the brain, helping to pinpoint any changes that might be indicative of Alzheimer's:
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) and Computed Tomography (CT) scans are used to rule out other conditions that could cause symptoms, such as strokes, tumors, or build-up of fluid in the brain.
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans can show the patterns of brain activity and whether amyloid proteins, a hallmark of Alzheimer's disease, are present in the brain.
Biomarker Tests
Recent advancements in medical science have led to the development of biomarker tests that can identify signs of Alzheimer's disease in brain fluids or imaging. These tests look for specific proteins associated with Alzheimer's disease processes, such as beta-amyloid and tau proteins, and can provide additional evidence to support a diagnosis.
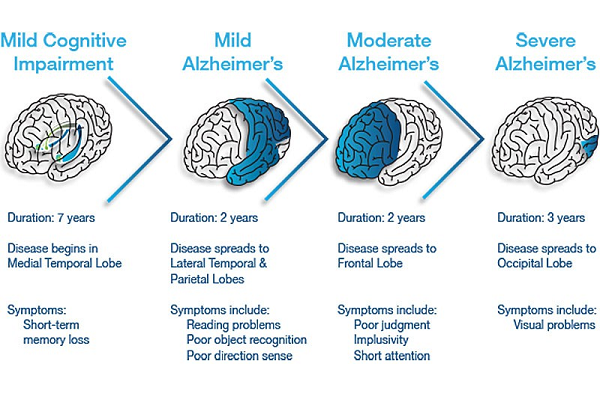
Alzheimer's disease progresses through several stages, each characterized by a decline in cognitive functions and daily functioning. Here’s a detailed look at the different stages of Alzheimer's disease based on the provided sources:
Preclinical Alzheimer's Disease
Stage 1: No Impairment (Preclinical Alzheimer's disease): In this stage, there are no noticeable symptoms, and the individual functions normally. However, changes are happening in the brain, such as abnormal accumulation of proteins, which may be detectable only through diagnostic tests like PET scans.
Early-Stage Alzheimer's (Mild Alzheimer's)
Stage 2: Very Mild Decline: Minor memory problems or losing things around the house may occur, which could be mistaken for typical age-related issues or overlooked.
Stage 3: Mild Cognitive Impairment: Friends and family may notice memory or concentration problems. At this stage, individuals may have trouble finding the right words, remembering names, or organizing and planning.
Middle-Stage Alzheimer's (Moderate Alzheimer's)
Stage 4: Moderate Cognitive Decline: Symptoms of dementia are clearly evident. Individuals may have difficulty with simple arithmetic, managing finances, recalling details about their life histories, and may withdraw from challenging social situations.
Stage 5: Moderately Severe Decline: Major gaps in memory and deficits in cognitive function emerge, which may require some assistance with day-to-day activities. Individuals might still remember significant details about themselves and their family but have difficulty performing tasks such as dressing appropriately.
Late-Stage Alzheimer's (Severe Alzheimer's)
Stage 6: Severe Decline: Memory continues to worsen, personality changes may take place, and individuals need extensive help with daily activities. At this stage, individuals may lose awareness of recent experiences and their surroundings, require assistance with dressing, toileting, and eating, and exhibit significant personality changes and potential behavioral problems.
Stage 7: Very Severe Decline: In the final stage, individuals lose the ability to respond to their environment, to carry on a conversation, and eventually control movement. They may still be able to utter words or phrases but need help with much of their daily personal care.
Understanding these stages helps caregivers and medical professionals manage the disease more effectively and plan appropriate care for the affected individual. For families looking for support and care options for loved ones with Alzheimer's, Medflyt provides specialized Alzheimer's care services in Manhattan, ensuring compassionate and competent care tailored to each stage of the disease.
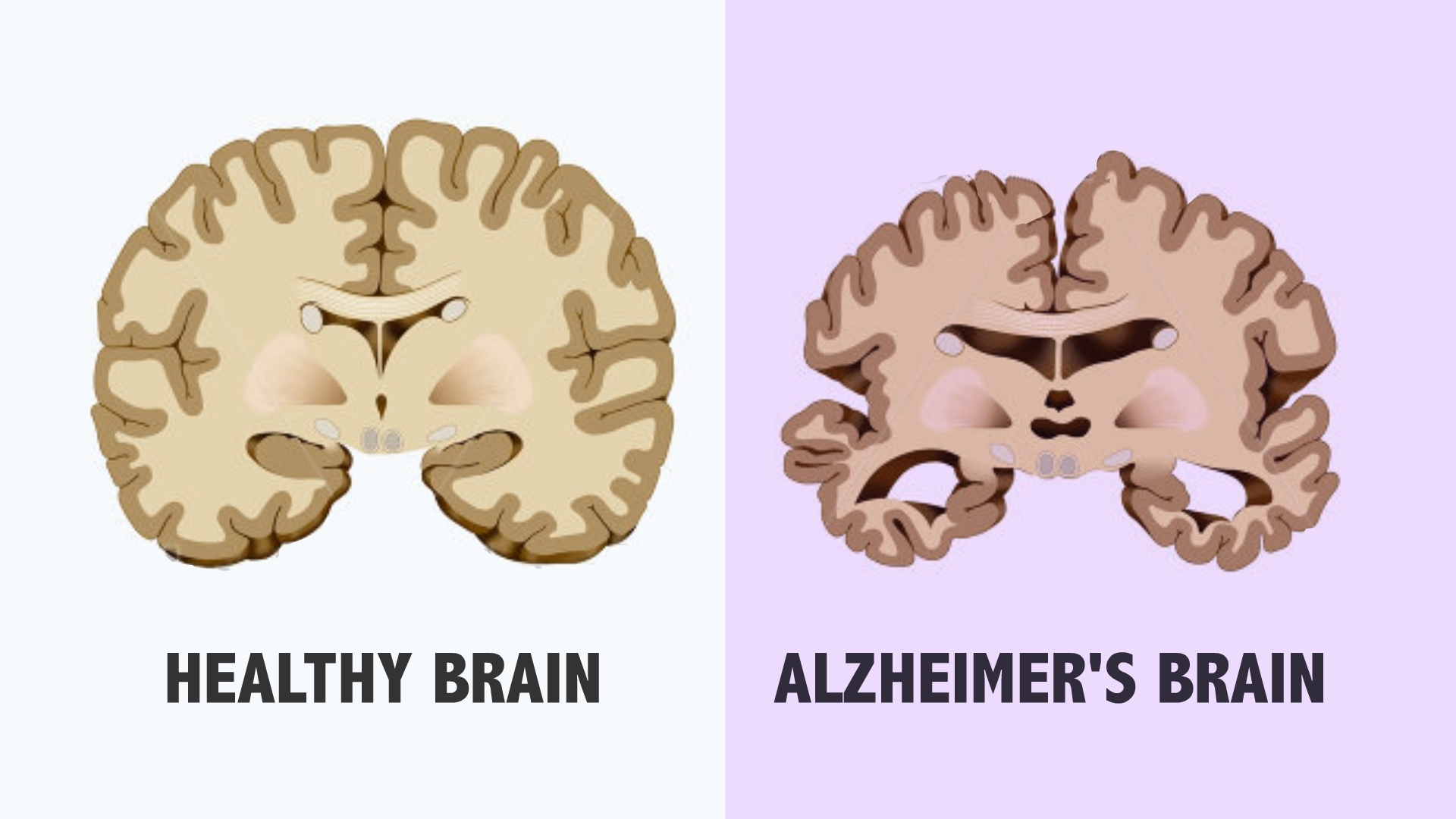
Conclusion
Diagnosing Alzheimer's disease is a complex process that involves a combination of medical evaluations, cognitive testing, and imaging studies. Early and accurate diagnosis can significantly improve the management of the disease, allowing for timely intervention and planning. For those in Manhattan seeking Alzheimer's care, Medflyt provides access to top-ranked licensed caregivers who specialize in Alzheimer's care, ensuring that your loved ones receive the best possible support in the comfort of their own homes.
